
Anthropometrics is the study of the human body and its movements. Especially in terms of its measurements. But ergonomics is the scientific discipline that involves designing products. And environments to match the individuals who use them. While anthropometrics involves the systematic measurement of the physical properties of the human body (height, weight, shape, arm length, etc.). Ergonomic involves incorporating anthropometric data. In designing products and environments. For instance, anthropometrics may involve measuring the circumference of heads of a target population. And obtaining an average value. Whereas ergonomics may use this average head circumference value to design safety helmets.
Anthropometrics involve research that includes measurements of the human body. While ergonomics involves using anthropometric data. When designing products to improve user experience. The primary difference between anthropometrics and ergonomics is their focus and use. Anthropometric data helps designers to design their products.

For instance, when designing a hairdryer. Measurements like the average height of users and the length of average arms. Become useful to decide the shape of the handle and the distance to be held from the head. When taking measurements from a target population for a specific product design. Designers generally derive an average value (midpoint) as the final measurement. Anthropometrics plays an important role in various fields such as furniture design, clothing design, architecture, and ergonomics.
Ergonomics is the scientific discipline of designing products and environments to match the people who use them. It incorporates anthropometric data when designing products to improve user experience. For example, when you manufacture a door handle. You use the measurements of the hand to design the shape and size of the handle. The same theory applies to designing various products such as furniture, vehicles, clothes, etc.
On occasions, designers don’t use anthropometric data in designing products. It may lead to users’ discomfort, pain, or even injury. Moreover, size, shape, weight, the position of controls, etc. Are measurements that contribute to ergonomic designing. In addition to anthropometric data, ergonomics also uses data from several disciplines. Such as biomechanics (muscles, forces, strength, levers) and environmental physics (noise, heat, cold, light, radiation, etc.)
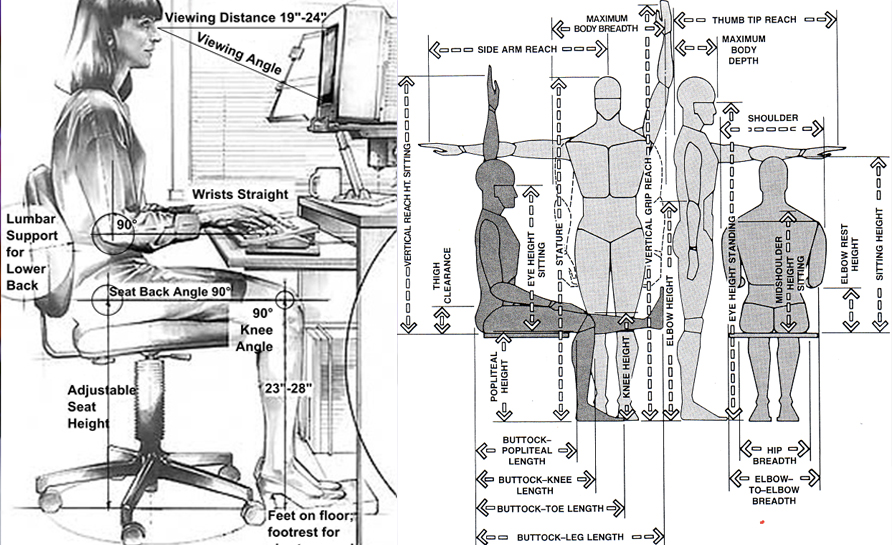
Physical ergonomics looks at how human anatomical, anthropometric, physiological, and biomechanical characteristics relate to physical activity. This includes:
To ensure that you keep your end users’ needs in focus at all times. You should make ergonomists an integral part of your design development team.